Encryption¶
Introduction¶
We give away important information/data alamost every day to the web. Therefore, it is important to who ever we are giving the information to to protect by encrypting the data. Encryption is when you convert plain text into cyphertext so that the plain text can only be understood by the authorized person. The translation of data into a secret code. To read an encrypted file, you must have access to a secret key or password that enables you to decrypt it.
History of Encryption¶
- The word encryption comes from the Greek word kryptos, meaning hidden or secret. People have been ecrypting text as early since the beginning of communication.
- Egyptians scribe used non-standard hieroglyphs to hide the meaning of an inscription.
- In 700 BC, the Spartans wrote sensitive messages on strips of leather wrapped around sticks.
- Until this point, all encryption schemes used Symmetric key. In 1976, B. Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman helped to solve one of the fundamental problems of cryptography, how to send the key to decypher the text without exposing the data/information.
- Then the RSA implemented the public-key cryptography using Asymmetric algorithms, or public-key.
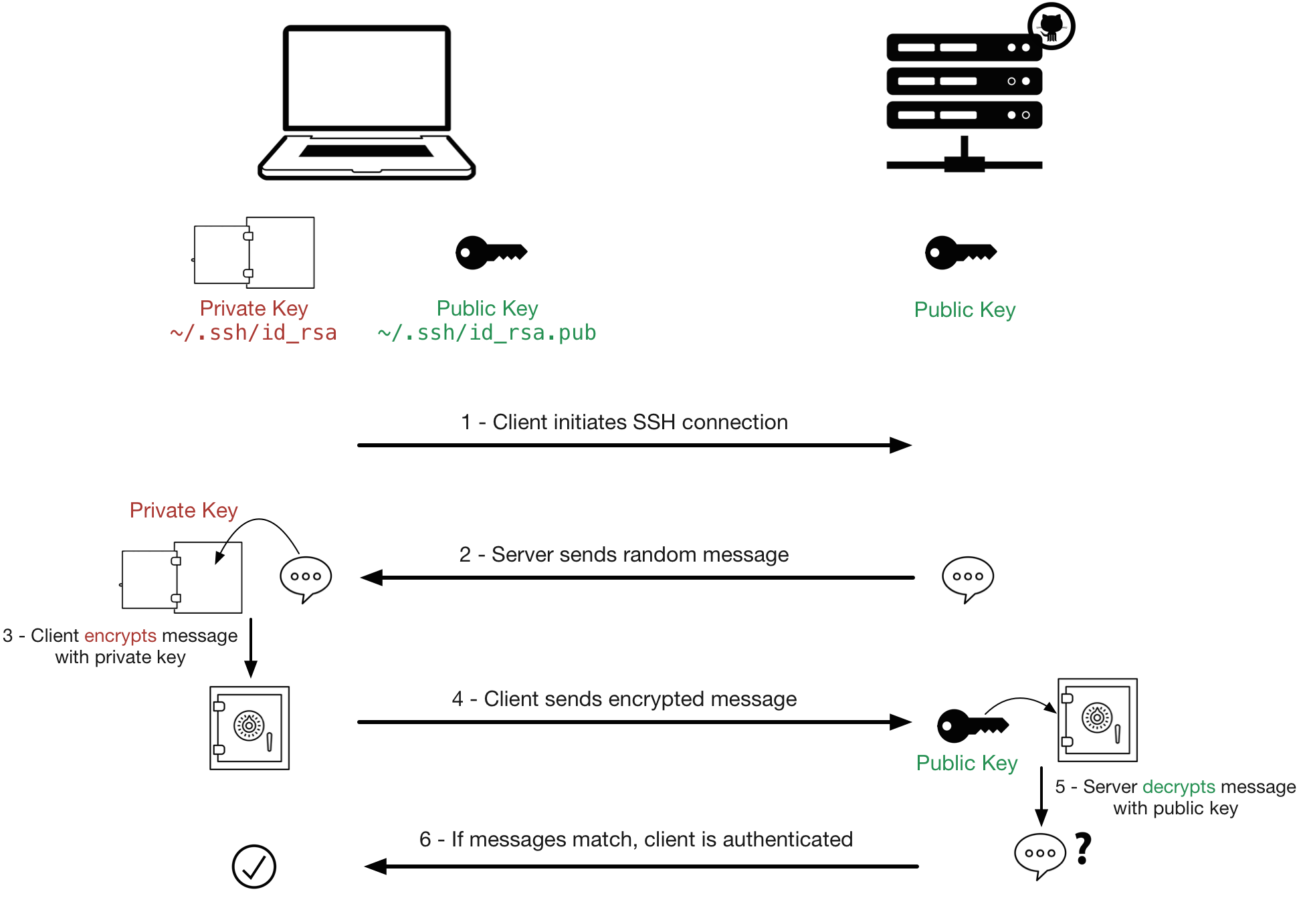
Different Kinds of Encryption¶
- Block Cipher: A block cipher is a method of encrypting text in which an algorithm is applied to a block of data at once as a group.
- Symmetric Key/ Secret key
- DES(Data Encryption Standard): A symmetric-key block cipher published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
- AES(Advanced Encryption Standard): A symmetric-key block cipher developed by two Belgian cryptopgrapher Joan Daemen and Vincent Rijmen.
- Asymmetric Key
- Diffie-Hellman: A method of securely exchanging cryptographic keys over a public channel. One of the first public-key protocols as originally conceptualized by Ralph Merkle and named after Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman
- Triple DES: Uses three individual keys with 56 bits each. The total key length is 168 bits, but experts would argue that 112-bits in key strength is more like it.
- RSA: Is considered an asymmetric algorithm due to its use of a pair of keys.
How We Use Encryption Today¶
Before there was assymetrical key, the officials were the only ones in need and using encryption. There was no need for someone else toe encrypt something because they were not sending information accross a network. Now, everywhere you have sensitive information needs to be encrypted, not only on your phone and laptop computer but in the ATM, websites, and servers.
Java code AES encryption example:¶
This is an example of how to implement AES encryption using java
aes_encryption_java_example.java:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 | import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Base64;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
public class AES {
//Initialize local variables.
private static SecretKeySpec secretKey;
private static byte[] key;
public static void setKey(String myKey)
{
MessageDigest sha = null;
try {
//Convert String to bytes
key = myKey.getBytes("UTF-8");
//Your sha are secure one-way hash functions that take arbitrary-sized
//data and output a fixed-length hash value.
sha = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-1");
//Takes in the key
key = sha.digest(key);
key = Arrays.copyOf(key, 16);
secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key, "AES");
}
catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static String encrypt(String strToEncrypt, String secret)
{
try
{
setKey(secret);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey);
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(cipher.doFinal(strToEncrypt.getBytes("UTF-8")));
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Error while encrypting: " + e.toString());
}
return null;
}
public static String decrypt(String strToDecrypt, String secret)
{
try
{
setKey(secret);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS5PADDING");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey);
return new String(cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(strToDecrypt)));
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Error while decrypting: " + e.toString());
}
return null;
}
}
|
Test AES encrypt/decrypt example¶
Let’s see an example of using AES encryption into java program with aes_encryption_decryption_java_example.java:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | public static void main(String[] args)
{
final String secretKey = "mysecretkey";
String originalString = "textIwantToEncrypt";
String encryptedString = AES.encrypt(originalString, secretKey) ;
String decryptedString = AES.decrypt(encryptedString, secretKey) ;
System.out.println(originalString);
System.out.println(encryptedString);
System.out.println(decryptedString);
}
|
Encryption example¶
There is a reason almost everything on your phone is encrypted now-a-days, because you have important information in your phone. Now, what could happen if someone could overpass that encryption and have access to the data and information on your phone. Last year in 2016, chipmaker Qualcomm's mobile processor that was used in 60% of Android had a flaw. In combination with a vulnerability with Android's media sever, together these vulnerabilities could allow someone with physical access to your phone to bypass the full disk encryption. Cited -----
..[image] "https://pixabay.com/en/encrypted-binary-file-computer-key-156514/"
| [encryption] | "What is encryption?." SearchSecurity. Web. 21 Feb. 2017. |
| [networking-class] | Paul Craven. "`Session Layer." <http://networking-class.readthedocs.io/en/latest/chapters/session_layer/session_layer.html>_. "Session Layer — Networking Class 2016 Fall documentation. Web. 21 Feb. 2017. |
| [webo] | Beal, Vangie. "Encryption." <http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/E/encryption.html>_.` What is Encryption? Webopedia Definition. Web. 21 Feb. 2017. |
Written by Esteban, Edited by Morgan and Sara.