Server Certificates¶
Written by Lana, Edited by Paul and Taylor.
Introduction¶
A server certificate is a digital certificate installed onto a web server. It is used for data encryption and to authenticate an organizational identity [GlobalSign]. Users will know if the website is secure due to the lock icon in the URL. For example, the screenshot below of Global Sign URL indicates it is a secure website.

Why Do Companies Need an SSL Certificate?¶
Companies need an SSL to encrypt the data the customer is entering such as username, password, credit card and more. This ensures clients that their sensitive information is not easily obtainable [GlobalSign]. If a server does not have a certificate, it cannot protect the clients from potentially being compromised.
SSL certificates are not only used to encrypt transactions, but to also verify the identity of the company. Clients are more likely to visit a trusted website such as Amazon, GameStop, U.S. Bank, and more. Therefore, it is highly recommended to have an SSL certificate. [GoDaddy]
What Could Happen if There is No SSL Certificate?¶
Login forms have sensitive information such as username and password. Furthermore, to create a new account on some websites requires an email and password which is also highly recommended to verify if the site is secure or not. If this is not properly secure, someone can easily obtain that information and read the data including the client's login information. Additionally, some users may use the same password for multiple sites. Therefore, the attacker can potentially compromise the user. [SSL-Shopper]
What Vulnerabilities are There?¶
There are websites that may appear legitimate, but are actually imposters. If the “real” company doesn’t contain an SSL, an imposter can affirm the certificate, resulting in users entering their sensitive information into a website that appears genuine but is actually fake. [Digicert]
Types of Certificates¶
Domain Validated Certificate
This type of certificate is mainly used for owning the domain name and verifying ownership. This type of certificate may be obtained for free, making it the cheapest kind. This is not commonly used for commercial purposes because it is a high risk certificate when used on a public website. The risk involves clients not able to verify the organization when they visit the website.[Symantec-Corp]_
Organization Validated Certificate
This type of certificate is a standard type of certificate that is used on commercial websites. Organization Validated Certificates are trusted because they are "authenticated by real agents against business registry databases hosted by governments" [Symantec-Corp]. This means that the website legitimatizes their business information.
Extended Validation Certificate
This type of certificate is the most trusted. This gives users peace of mind because the domain is a secured website. In addition, it has more defined guidelines for companies to follow. Basically, it encrypts all data between the user and web server. [Symantec-Corp]
How to Obtain an SSL Certificate?¶
A SSL Certificate can be purchased through a domain provider such as GoDaddy, DigiCert, GlobalSign and more. They will offer several different service packages including standard SSL certificate, Extended Validation Certificate, Multiple-Domains, and Wildcard(s). This is going to vary among company depending on what the company's end goal is for their website.
How to Tell if a Website is Secure?¶
There are several indications that can help identify if the website is secure.
1. Check to see if the URL has a lock on it. Depending on which browser, it will display a lock icon either left of the URL (Firefox and Chrome) or right (Internet Explorer). In the event that the website is secure, it will have "https" at the beginning of the URL (except Internet Explorer, which only has the lock icon). Furthermore, select the lock icon and it will say "this is a secure connection".

This screenshot is an example of an unsecure website. Even though the information is not extremely sensitive in this example, it is good practice to be cautious of what information is being entered.
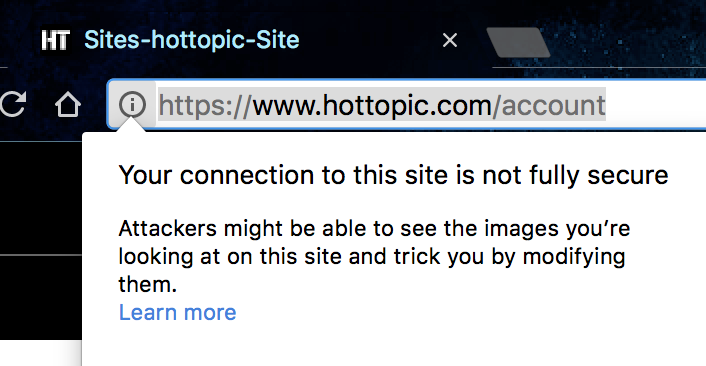
This screenshot is of the login page on Hot Topic's website. Even though it says https, this is an indication that not all data on the webpage is encrypted and some of the content is readable. However, the information that is being inputted into the email and password is secure. The screenshot below explains what is not encrypted on the webpage.
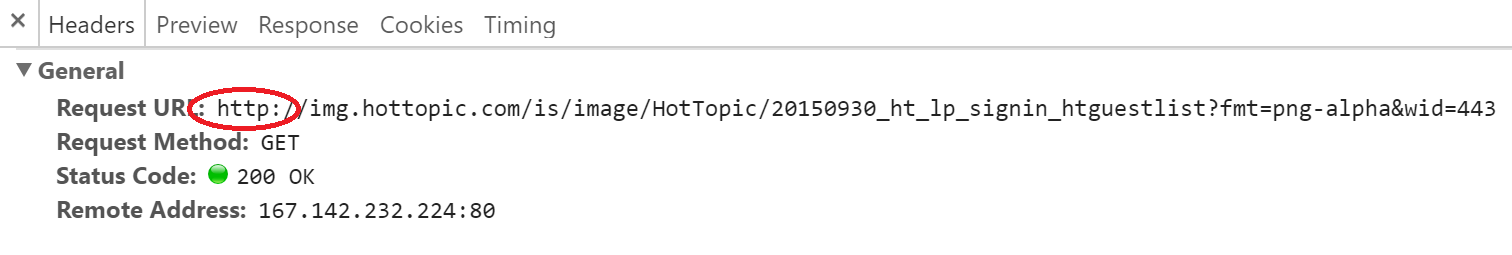
This screenshot on Hot Topic's website is the reason why the login page is considered "not fully secure". It is a image that is using HTTP and not HTTPS.

This screenshot of Amazon.com displays that it is a secure website. Before the URL, it has a lock icon with the word "Secure" to identify that all information will be encrypted.
2. Always verify the domain. It is possible to visit a website that looks like the real company, however, but it is the imposter. For example, a suspicious email from U.S. Bank states the account has not been verified, and to click on the following link. This is where the first mistake occurs. Do not click on the URL provided within the email because it could be directed to a whole other website. To check this, hover the mouse cursor over the link and it will display the true URL. Phishing attempts occur often and they will imitate the real company to their best ability to deceive the clients.
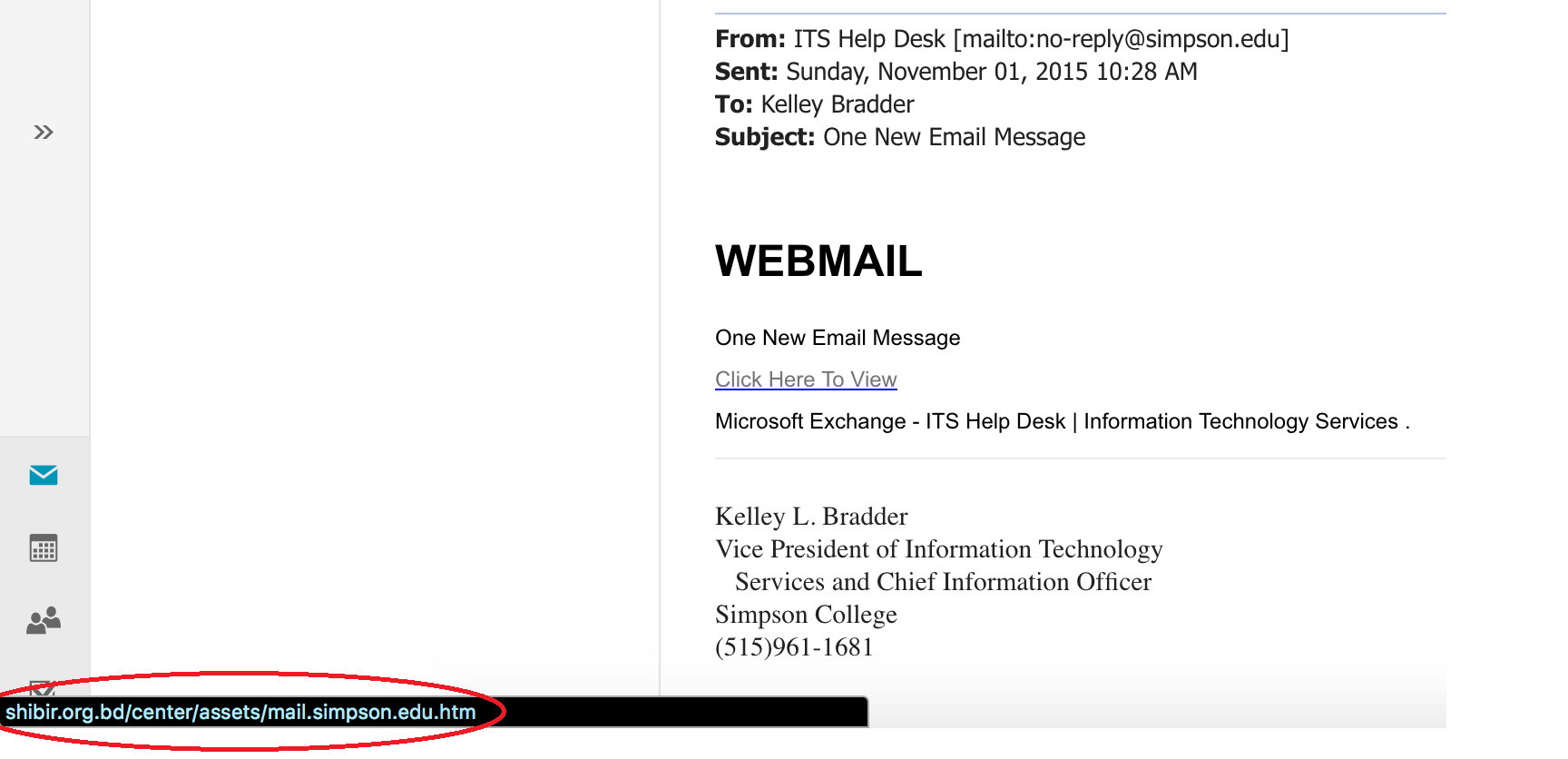
In this example, Simpson students may have received an email saying "One New Email Message" from Kelley Bradder. However, hover the mouse over the link, and it will expose the true website that the students would have been directed to.
3. Be a wise shopper. If the prices are too low, it is too good to be true. It is advised to only shop at reputable websites such as Amazon. In contrast sometimes companies could fail to update their certificate. So if a website that previously had a valid certificate, it will warn end users that the website security certificate presented is not valid. Under those circumstances there will be a chance hackers to intercept the data. So either wait for the company to renew their certificate or visit another.
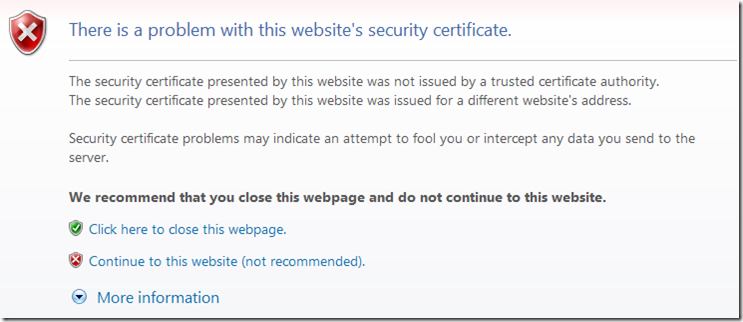
If a SSL certificate expires the end users will be greeted by this warning. [Microsoft]
Alternatively, an application that requires a SSL certificate functions the same way. Apple made a recent change in the last year requiring all apps from the Mac App store to have a "valid provisioning profile" that must be updated periodically [Mac]. For those who did not renew it on time saw the consequences which the application would crash not allowing users to open it. Developers were aware of the changes, but did not think it applied to them. As a matter of fact, the recent policy changes by Apple did impact several applications, but developers were not aware until it occurred.
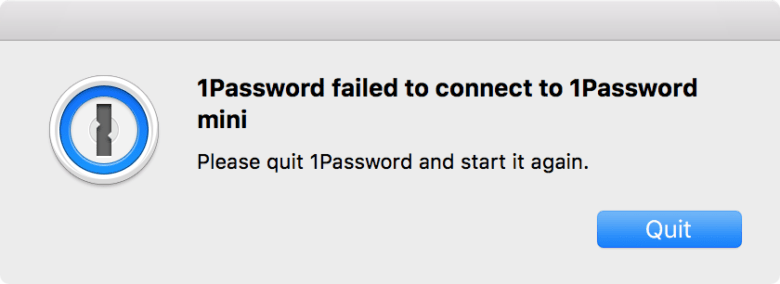
One Password is a popular application on Apple where users have a vault that stores all of their passwords. This was one of the many applications that did not renew their certificate resulting in the app crashing everytime the end user attempted to open it. [Mac]
Keep in mind, not all websites need an SSL certificate due to the type of content. For example, IMDB is an informative website about movies, T.V. shows, and actors/actresses. Therefore, IMDB made the decision to have the SSL Certificate to be applied only when the user is logging into their account and when viewing their profile. Otherwise, the remainder of the website is unsecure. Basically, it is ok for some websites to not have all content to be secure. Regardless, it is crucial to verify if the webpage is secure when entering sensitive information and purchasing products online.
Sources¶
| [Digicert] | "Protect Yourself Against Fraudulent SSL Certificates." What Are Fraudulent SSL Certificates & How Can Users Protect Themselves. Digicert, n.d. Web. 21 Feb. 2017. <https://www.digicert.com/protecting-against-fraudulent-certificates.htm>. |
| [GlobalSign] | (1, 2) "GlobalSign." SSL & Digital Certificates by GlobalSign., n.d. Web. 20 Feb. 2017. <https://www.globalsign.com/en/ssl-information-center/what-is-an-ssl-certificate/>. |
| [GoDaddy] | "Do you need SSL encryption if you don't sell anything on your website?" GoDaddy., 16 Jan. 2017. Web. 21 Feb. 2017. <https://www.godaddy.com/garage/smallbusiness/secure/do-you-need-ssl-encryption-if-you-dont-sell-anything-on-your-website/>. |
| [SSL-Shopper] | "Do I Need An SSL Certificate For My Website?" Do I Need An SSL Certificate For My Website? SSL-Shopper, n.d. Web. 21 Feb. 2017. <https://www.sslshopper.com/article-do-i-need-an-ssl-certificate-for-my-website.html>. |
| [Symantec-Corp] | (1, 2) "Types of SSL certificates – choose the right one." Symantec - Global Leader In Next-Generation Cyber Security. Symantec, n.d. Web. 23 Feb. 2017. <https://www.symantec.com/connect/blogs/types-ssl-certificates-choose-right-one>. |
| [Microsoft] | Sanders, Jeff. "Troubleshooting ASP.NET – The remote certificate is invalid according to the validation procedure." Http Client Protocol Issues (and other fun stuff I support). Microsoft, n.d. Web. 27 Feb. 2017. <https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/jpsanders/2009/09/16/troubleshooting-asp-net-the-remote-certificate-is-invalid-according-to-the-validation-procedure/>. |
| [Mac] | (1, 2) "Some popular Mac apps fail as developer certificates expire." Cult of Mac. Cult of Mac, 20 Feb. 2017. Web. 27 Feb. 2017. <http://www.cultofmac.com/468457/mac-apps-failing-developer-certificates-expire/>. |